NPTEL Wastewater Treatment And Recycling Week 1 Assignment Answer 2024
Q1. What is wastewater recycling?
a. Treating wastewater for removal of contaminants
b. Recovering beneficial nutrients or metals from wastewater
c. Reclaiming water from wastewater and putting it to beneficial (re)uses
d. All of the above
Answer:- For Answer Click Here
Q2. Wastewaters generated from is not a component of Greywater:
a. Kitchen
b. Toilet
c. Laundry
d. Bathroom
Answer:- For Answer Click Here
Q3. Identify the correct statements regarding potential recoveries from wastewater:
Statement I: Through adequate treatment, usable water may be reclaimed from wastewaters.
Statement II: Wastewater can also be processed for recovery of energy as well as nutrients.
a. Statement I is correct, while statement II is incorrect
b. Statement Il is correct, while statement I is incorrect
c. Both, statements I and II are correct
d. Both, statements I and II are incorrect
Answer:-
Q4. A non-point pollution source means:
a. A source with negligible amount of pollution
b. A set of several small sources from many different locations
c. A source of pollution that was there is past, but no more exists
d. A hidden source of pollution which can’t be identified
Answer:- For Answer Click Here
Q5. Which of the following is an example of point source of pollution:
a. Discharge of industrial effluent
b. Discharge from sewage treatment plant
c. Spill from oil refinery
d. All of the above
Answer:-
Q6. Identify non-point sources of pollution among followings:
a. Urban and agricultural runoffs
b. Spill from oil refinery
c. Discharges from ETPs and STPs
d. All of the above
Answer:-
Q7. Identify the correct statements regarding linkage of waterborne diseases with poor wastewater management.:
Statement I: Waterborne diseases are common in regions with poor wastewater management.
Statement II: Direct consumption of wastewater is the major reason for the spread of waterborne diseases in such regions.
a. Statement I is correct, while statement Il is incorrect
b. Statement II is correct, while statement I is incorrect
c. Both, statements I and II are correct
d. Both, statements I and II are incorrect
Answer:- For Answer Click Here
Q8.
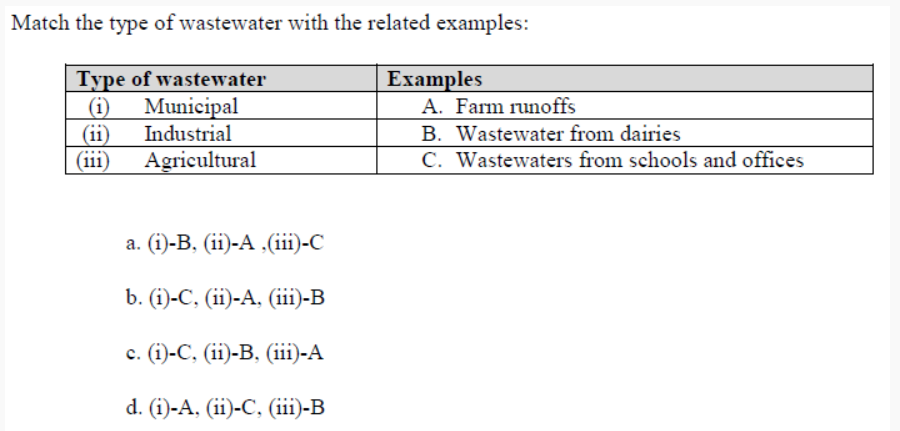
Answer:-
Q9. Why greywater is relatively easier to treat (compared to treating municipal sewage) for reuse applications?
a. Greywater is easier to collect and transport to treatment facility
b. Greywater is less in quantity
c. Greywater has less pollution load
d. There are dedicated technologies for greywater treatment
Answer:- For Answer Click Here
Q10. Often, in centralized wastewater management systems:
a. Several smaller size treatment facilities are needed
b. Long distance transport of wastewater is required
c. Quality control is difficult
d. All of the above
Answer:-
NPTEL Wastewater Treatment And Recycling Week 4 Assignment Answer 2023
1. Self-purification processes in rivers, refers to:
a. Installing in-situ sediment filters for contaminant removal in rivers
b. Setting up in-stream natural–processes based treatment systems in rivers
c. Dosing chemicals to the rivers which leads to precipitate and remove
pollutants
d. Naturally-occurring processes in rivers which reduces the pollutant levels in river water
Answer :- For Answer Click Here
2. Match the type of processes for contaminant fate and transport given in first column with the specific process given in second column:
Type of process
(i) Mass Transport
(ii) Phase Transfer
(iii Transformation
Contaminant Fate and Transport Processes
A. Biodegradation
B. Dispersion
C. Volatilization
a. (i)-B, (ii)-A.(iii)-C
b. (i)-B. (ii)-C. (iii)-A
c. (i)-C, (in)-A. (ill)-B
d. (1)-A. (in)-C. (il)-B
Answer :-
3. After the point of discharge of a wastewater stream, the first zone to appear in a river is:
a. Decomposition Zone
b. Septic Zone
c. Recovery Zone
d. Reaeration Zone
Answer :- For Answer Click Here
4. For a river receiving wastewater discharge, the most critical stretch is considered, where:
a. DO is minimum
b. DO is maximum
c. BOD is minimum
d. BOD is maximum
Answer :- For Answer Click Here
5. The Streeter Phelps Equation is used to describes the variation of DO in a stream receiving wastewater discharge. Which of the following assumptions is correct about the classical Streeter Phelps Equation?
a. The flow pattern in the river follows plug-flow
b. Only re-aeration is taken as the source of DO in the river water
c. Only carbonaceous BOD is considered responsible for DO consumption
d. All of the above
Answer :-
6. Identify the correct statements regarding conservative pollutants:
Statement I: Conservative pollutants are non-degradable, thus stable and persistent in nature.
Statement II: Since conservative pollutants are not degraded in nature, it poses lesser environmental risk than non-conservative pollutants.
a. Statement I is correct. while statement II is incorrect
b. Statement II is correct. while statement I is incorrect
c. Both. statements I and II are correct
d. Both. statements I and II are incorrect
Answer :-
7. Consider the following generic mass balance equation (in usual notations):

Answer :-
8. For mass balance equation in a Continuous Stirred Tank Reactor (CSIR):
a. Inflow and outflow flux is considered as zero
b. Reaction term in the mass balance equation is considered as zero
c. The outflow concentration of contaminant is taken same as the concentration
in the reactor
d. All of the above
Answer :-
9. If the reaction kinetics in a mass balance equation is expressed as dCIdt = k.C”, the order of the reaction is:
a. First order
b. nt order
c. Ct order
d. It order
Answer :-
10. Mixing or no-mixing in a reactor guides in identifying:
a. Conservative or reactive nature of pollutant
b. Steady or unsteady state in the reactor
c. Batch or continuous flow process
d. Plug flow conditions in the reactor
Answer :-
11. A plug-flow reactor of volume 250 m’ is operating under steady state at 16 m°h flow of a wastewater stream having influent BODs as 360 mg/L. If the BOD decay rate constant is 0.141 per hour, the outlet BOD Concentration would be:
a. 20 mg/L
b. 40 mg/L
c. 80 mg L
d. 160 mg/I
Answer :-
12. A mixed tank reactor is to be designed for treating phenol in an industrial wastewater, form an initial concentration of 70 mg/L to a final outlet concentration of 5 mg/L, where phenol is expected to undergo first order decay at a rate constant of 0.65/d. If the reactor is to be operated at steady state, the design volume of reactor for treating 20 kL/d wastewater would be:
а. 135 m3
b. 294 m3
с. 400 m°
d. 620 m
Answer :- For Answer Click Here
Question Statement (13-15): The 5-day BOD of a wastewater sample measured at 20°C incubation temperature was found to be 320 mg/L. The laboratory data revealed that the BOD reaction rate constant (at 20°C) k2o (base e) was 0.26/day, and the temperature coefficient was 1.035. Based on the information. answer the following questions:
13) The ultimate BOD of wastewater, at 20°C incubation temperature, is (in mg/L)
Answer :-
14. The 3-day BOD of this wastewater, at 20°C incubation temperature, is (in mg/L)
Answer :-
15. The 3-day BOD of this wastewater. at 27°C incubation temperature. is (in mg L):
Answer :- For Answer Click Here
NPTEL Wastewater Treatment And Recycling Week 3 Assignment Answer 2023
1. Turbidity in water is usually measured based on:
a. Measuring rate constant of chemical reactions
b. Gravimetric measurements (by weighing)
c. Detecting scattering of light passed through water
d. Detecting potential for conducting electric current
Answer:-
2. Spectrophotometers are typically used to measure:
a. Redox potential
b. Colour
c. Conductivity and TDS
d. All of the above
Answer:-
3. At 20 °C temperature, and atmospheric pressure, the saturation dissolved oxygen level in water is approximately:
a. 9 mg/L
b. 2 mg/L
c. 0.5 mg/L
d. Zero
Answer:-
4. DO vary with water temperature and altitude, as:
a. Cold water holds more oxygen than warm water, and water at lower altitudes holds less oxygen than water at higher altitudes
b. Cold water holds less oxygen than warm water, and water at lower altitudes holds less oxygen than water at higher altitudes
c. Cold water holds more oxygen than warm water, and water at lower altitudes holds more oxygen than water at higher altitudes
d. Cold water holds less oxygen than warm water, and water at lower altitudes holds more oxygen than water at higher altitudes
Answer:-
5. The pH of a water sample was measured as 6.4 unit. The measured total alkalinity and measured total acidity of water would be:
a. Total Alkalinity = 0; Total Acidity = 0
b. Total Alkalinity = 0; Total Acidity > 0
c. Total Alkalinity > 0; Total Acidity = 0
d. Total Alkalinity > 0; Total Acidity > 0
Answer:-
6. Among the given options, the likeliest value of BOD of a wastewater sample, having 450 mg/L COD, is:
a. Zero
b. 270 mg/L
c. 450 mg/L
d. 700 mg/L
Answer:-
7. Match the type of effects of improper wastewater management with the related examples:
Class of pollutants in wastewater
(i) Organic pollutants
(ii)Emerging Contaminants
(iii) Nutrients
Examples
A. BOD and COD
B. Orthophosphate and nitrate
C. Antibiotics and pesticides
a. (i)-B. (ii)-A .(ini)-C
b. (i)-C. (ii)-A. (iii)-B
c. (i)-C. (ii)-B. (iii)-A
d. (i)-A. (ii)-C. (iii)-B
Answer:-
8. The BODs values of two wastewater samples A and B were measured as 80 mg/L and 210 mg L, respectively. This signifies that:
a. Sample A has lesser biodegradable organic matter load than Sample B.
b. Sample A has higher biodegradable organic matter load than Sample B.
c. Sample A has less quantity of biomass present than that in Sample B
d. Sample A has more quantity of biomass present than that in Sample B
Answer:-
9. Identify the correct statements regarding emerging contaminants, or contaminants of emerging concern: Statement
I: Emerging contaminants are generally bioaccumulative, but are non- persistent, and have very less toxicity. Statement
II: Emerging contaminants have become relatively easily identifiable with the new techniques for chemicals identification and separation.
a. Statement I is correct, while statement II is incorrect
b. Statement II is correct. while statement I is incorrect
c. Both, statements I and II are correct
d. Both, statements I and II are incorrect
Answer:-
10. A wastewater contains 180 mg L acetic acid (CH;COOH). The contribution of acetic acid to the theoretical COD of this wastewater is [Governing oxidation reaction: CH&COOH + 202 = 2H20 + 2C02]
a. 76 mg/L
b. 180 mg/L
c. 192 mg/L
d. 360 mg/L
Answer:-
11. 5 mL of a wastewater sample was diluted with aerated distilled water, made up to 300 mL in a BOD bottle. The initial DO was measured as 8.2 mg L, which dropped to 1.8 mg/L in 5 days’ time. BODs of the sample is:
a. 384 mg/L
b. 256 mg/L
c. 180 mg/L
d. 64 mg/L
Answer:-
12. In a MPN Test, 10 mL, 1 mL, and 0.1 mL of wastewater was inoculated in 5 replicates in nutrient broth, and resulted in 5, 2 and 0 positives tests, respectively, after 48 hrs of incubation. The MPN index / 100 mL of the wastewater would be (use the 5-replicates MPN table):
a. 20
b. 49
c. 70
d. 112
Answer:-
Question Statement (13-15): A 100 mL wastewater sample was filtered using a GF/C filter paper of weight 1.750 g and the filtrate collected in a silica crucible of weight 24.802 g. Both, crucible and filter paper were dried for 24 hr in an oven at 104 °C. Post drying, the weight of the filter paper and crucible was measured as 1.924 g. and 24.928 g. respectively. Thereafter, both crucible and filter paper were placed in muffle furnace for 20 mins at 550 °C. Post ignition, the weight of the filter paper and crucible was measured as 1.842 g, and 24.866 g. respectively. Bases on the data, answer the followings:
13. The Total Suspended Solids (TSS) concentration in the wastewater is (in mg L)
Answer:-
14. The Volatile Suspended Solids (VSS) concentration in the wastewater is (in mg/L)
Answer:-
15. The Total Solids (TS) concentration in the wastewater is (in mg/L):
Answer:-
NPTEL Wastewater Treatment And Recycling Week 2 Assignment Answer 2023
1. The quantity of municipal wastewater generated from a city depends on:
a. Population of the city
b. Water consumption pattern of the inhabitants
c. Both, population and water consumption pattern
d. Neither population nor the water consumption pattern
Answer :- c
2. Dry Weather Flow is:
a. The actual flow of sanitary sewage
b. The stormwater contribution to sewers in dry season
c. Combined stormwater flow plus sanitary sewage flow
d. Quantity of sanitary sewage flow subtracted from stormwater flow
Answer :- a
3. Identify the correct statements regarding design capacity of sewer systems:
Statement I: Incorrect estimation of the quantity of sewage generated may lead to
inadequate or hydraulically inefficient sewer system design.
Statement II: Under-estimation of the design sewage flow will make the system uneconomical.
a. Statement I is correct, while statement II is incorrect
b. Statement II is correct, while statement I is incorrect
C. Both, statements I and II are correct
d. Both, statements I and II are incorrect
Answer :- a
4. Design period of various sewerage components are usually based on:
a. Availability of funds for design
b. Useful life of the specific components
c. The duration of the sewerage services required
d. Average life of the sewerage facility
Answer :- b
5. Which of these population forecasting method is likely to overestimate the forecasted population for a city of moderate size and age:
a. Arithmetic Increase Method
b. Incremental Increase Method
c. Geometric Increase Method
d. Logistic Growth Method
Answer :- c
6. Using Growth Composition Analysis Method (Demographic Method), population is estimated based on annual birth rate, death rate and migration rates. Which of these is relatively the most difficult to estimate:
a. Birth rate
b. Death rate
c. Migration rate
d. All of the above
Answer :- c
7. The peak factor is used to estimate peak for sewer designs. The correct relation between peak factor for sewage flow estimation with the increase in population, is:
a. Peak factors have large fluctuations for highly populated cities
b. Peak factor is independent of population increase
c. Peak factor typically increased with the increase in population.
d. Peak factor typically decreases with the increase in population.
Answer :- d
8. Population forecast in a logistic growth model is limited by the:
a. Availability of the master plan of the region
b. Exponential growth rate of the population
c. Migration rate of the population
d. Population carrying capacity of region
Answer :- d
9. As per CPHEEO Manual (20212), the conventional sewers shall be designed for a minimum sewage flow of:
a. 30 litres per capita per day
b. 55 litres per capita per day
c. 100 litres per capita per day
d. 250 litres per capita per day
Answer :- c
10. Which of the these may lead to additional inflow to sewer lines?
a. Water used from unaccounted private water supplies
b. Water used for gardening and horticulture
c. Water losses from water supply systems
d. All of the above
Answer :- a
Question Statement (11-13):
The population of a city was recorded as 2.5 lakhs, 3.2 lakhs, 4.1 lakhs, and 5.2 lakhs in
1991, 2001, 2011, and 2021, respectively. Based on the data, answer the following:
11. The forecasted population in 2041 using arithmetic increase method, would be (in Lakhs)
Answer :- 6.6,7.4
12. The forecasted population in 2041 using arithmetic increase method, would be (in Lakhs)
Answer :- 8,9
13. The forecasted population in 2041 using arithmetic increase method, would be (in Lakhs)
Answer :- 7.2,8
14. A city with 12 lakh populations receives 150 lped water supply. Assuming that 80% of the water used is received as municipal sewage, the maximum daily flow of sewage from the city, assuming a daily peak factor of 2, would be:
a. 360 MLD
b. 288 MID
c. 180 MLD
d. 72 MLD
Answer :- b
15. The average daily sewage flow from city is 16 MLD. Assuming daily and hourly peak factor as 2 and 1.5, respectively, the maximum (peak) hourly flow of the sewage would be:
a. 172 m°/h
b. 768 m3д
c. 1240 m’h
d. 2000 m3д
Answer :- d
NPTEL Wastewater Treatment And Recycling Week 1 Assignment Answer 2023
1. Which of the following component of wastewater is often not considered as a resource?
a. Water
b. Nutrient
c. Organic matters
d. Pathogens
Answer :- d. Pathogens Pathogens are microorganisms, such as bacteria, viruses, and parasites, that can cause diseases. While other components of wastewater like water, nutrients, and organic matter can be treated and potentially reused or recycled, pathogens are typically not considered a resource due to their potential to pose health risks if not properly treated and removed from wastewater. The focus is on eliminating or reducing pathogens to prevent the spread of diseases rather than utilizing them as resources.
2. Wastewater generated from laundry and showers are typically referred as:
a. Brown water
b. Greywater
c. Black water
d. Stormwater
Answer :- b. Greywater Wastewater generated from laundry and showers is typically referred to as greywater. Greywater is the relatively clean wastewater that comes from non-toilet fixtures, such as sinks, showers, bathtubs, and laundry machines. It contains fewer contaminants compared to "black water" (toilet wastewater), and it can be treated and reused for purposes like irrigation, flushing toilets, and other non-potable uses.
3. Identify the correct statements regarding non-point sources of pollution:
Statement I: Non-point pollution sources are usually difficult to monitor and control
in comparison to point sources
Statement II: The individual as well as collective contributions of the non-point
sources are always small.
a. Statement I is correct. while statement Il is incorrect
b. Statement II is correct, while statement I is incorrect
c. Both, statements I and II are correct
d. Both, statements I and II are incorrect
Answer :- a
4. Sort the following in Point and Non-Point sources of pollution:
i. Industrial Effluent
ii. Urban runoff
iii. Discharge from sewage treatment plant
iv. Atmospheric deposition
a. Point Sources – i, iv; Non-Point Sources – ii, iii
b. Point Sources – i. iii: Non-Point Sources – ii. iv
c. Point Sources – ii. iii: Non-Point Sources – i. iv
d. Point Sources – ii, iv; Non-Point Sources – i. iii
Answer :- b
5. Adequate wastewater treatment may result in the recovery of:
a. Reclaimed water
b. Nitrogen and Phosphorous
c. Energy
d. All of the above
Answer :- d
6. Which of these is included in greywater:
a. Toilet flush
b. Urine
c. Kitchen drain
d. All of the above
Answer :- c
7. Identify the correct statements regarding contaminants and pollutants:
Statement I: A pollutant always has harmful effects on the surroundings while a contaminant may or may not have the same.
Statement II: A pollutant may be a component of the system while a contaminant is usually introduced from the outside.
a. Statement I is correct. while statement II is incorrect
b. Statement II is correct, while statement I is incorrect
c. Both, statements I and II are correct
d. Both, statements I and II are incorrect
Answer :- c
8. An example of the direct impact of inadequately managed wastewater on the ecosystem is
a. Eutrophication
b. Climate Change
c. Acid Rain
d. All of the above
Answer :- a
9. Which of this is not a technique for the wastewater treatment?
a. Septic Tank
b. Settling and filtration
c. Dilution with freshwater
d. Biological processing for organic contaminants breakdown
Answer :- c
10. Match the type of effects of improper wastewater management with the related examples:

a. (1)-B, (ii)-A (in1)-C
b. (i)-C. (ii)-A. (iii)-B
c. (i)-C. (ii)-B. (iii)-A
d. (i)-A. (ii)-C. (ini)-B
Answer :- b
11. Which of the following wastewater types are relatively easiest to treat for reuse applications?
a. Municipal sewage
b. Black water
c. Greywater
d. Industrial effluent
Answer :- c
12. Which of the following is more adequate as an example of wastewater reuse in environmental sector?
a. Discharge of treated sewage to agricultural fields
b. Discharge of untreated sewage to a river
c. Treated wastewater recycling for toilet flushing
d. Artificial groundwater recharge with treated sewage
Answer :- d
13. Typically, pollution load is considered highest in:
a. Municipal Wastewater
b. Industrial Wastewater
c. Agricultural Wastewater
d. Stormwater
Answer :- b
14. Which of the following is India’s central government programme does include wastewater or greywater management as one of their components?
a. Swachh Bharat Mission
b. National Mission for Clean Ganga
c. Jal Jeevan Mission
d. All of the above
Answer :- d
15. Identify the CORRECT statements regarding decentralized wastewater management:
a. Recycling of wastewater is comparatively easier
b. Disposal or treatment location may be far away from the origin point
c. Large wastewater treatment plant is needed
d. Long-distances transport of sewage is needed
Answer :- a
NPTEL Wastewater Treatment And Recycling Assignment Answer Week 1 2022
1. Wastewater is considered a potential resource because:
a. 99 % of wastewater comprises water
b. The pollution content of wastewater is very high
c. Wastewater processing to remove contaminants is fairly easy
d. Reclaimed wastewater is readily accepted by consumers for reuse
Answer :- a. 99 % of wastewater comprises water
2. Which of the following is NOT a non-point source of wastewater pollution?
a. Sediment overflow from eroding stream banks
b. Large sanitary landfills
c. Nutrients from livestock and pet waste
d. Irrigation runoff from agricultural lands
Answer :- b. Large sanitary landfills
3. Which of the following is correct for domestic wastewater composition?
a. Greywater + blackwater
b. Greywater + brownwater
c. Brownwater + Urine
d. Heavy greywater + blackwater
Answer :- a. Greywater + blackwater
4. Which of the following is a component of blackwater?
a. Urine
b. Feces
c. Flush water
d. All of the above
Answer :- d. All of the above
5. Identify the CORRECT statement concerning pollutants and contaminants.
a. Pollutants may or may not create harmful effects
b. Pollutants are foreign matter, typically introduced from outside
c. Contaminants may or may not create harmful effects
d. Contaminants are either harmful or poisonous in nature
Answer :- c. Contaminants may or may not create harmful effects
6. Non-point sources of pollution are usually difficult to monitor and control because:
a. Many small diffuse sources from different locations comprise such sources
b. Requires several spatially-distributed monitoring stations
c. Difficult to determine the dispersion rates of pollutant flow rates
d. All of the above
Answer :- d. All of the above
7. Which of the following is NOT an ideal practice of wastewater recycling?
a. Use of treated domestic wastewater for horticulture
b. Discharge of treated domestic sewage into agricultural fields
c. Use of treated industrial effluent in cooling towers
d. Discharge of domestic sewage into irrigation channels
Answer :- d. Discharge of domestic sewage into irrigation channels
8. Degradation of natural aquatic ecosystems due to poor water management may lead to:
a. Eutrophication
b. Dead zones
c. Both a. and b.
d. Putrefaction
Answer :- c. Both a. and b.
9. Which of the following central government schemes is aimed at attaining nationwide cleanliness and hygiene?
a. Swachh Bharat Abhiyan
b. Unnat Bharat Abhiyan
c. Namami Gange
d. None of the above
Answer :- a. Swachh Bharat Abhiyan
10. Constructed wetlands can be used for:
a. Water conservation
b. Preservation of flora and fauna
c. Wastewater treatment
d. All of the above
Answer :- d. All of the above
11. A resource management option to recover energy from wastewater is:
a. Protein feed for livestock
b. Wetland technology
c. Biomass production
d. Agricultural irrigation
Answer :- c. Biomass production
12. A prominent disadvantage of decentralized wastewater management systems is:
a. Higher number of sewage treatment plants
b. Considerably longer duration of sewage transport
c. Difficulty of recycling treated effluent
d. Difficulty related to operations and maintenance
Answer :- a. Higher number of sewage treatment plants
13. A common water-borne disease caused by pathogenic microbes spread via poor wastewater treatment is:
a. Diarrhea
b. Typhoid
c. Cholera
d. All of the above
Answer :- d. All of the above
14. Identify the INCORRECT statements concerning the negative impacts of poor wastewater management.
I. Poor wastewater management is likely to increase the cost of drinking water treatment
II. Increased greenhouse gas emissions are a possible positive impact of poor wastewater management
III. Poor wastewater management may supposedly also result in decreased biodiversity in the long run
a. Only statement I is correct
b. Only statement II is incorrect
c. Statement I and II are incorrect
d. All statements are incorrect
Answer :- b. Only statement II is incorrect
15. Which of the following is NOT true for centralized wastewater management systems?
a. Large wastewater treatment plants are needed in centralized systems
b. Fresher sewage is difficult to obtain in centralized systems
c. Recycling sewage is comparatively easy in centralized systems
d. Centralized systems are preferred for communities with fewer options for effluent reuse.
Answer :- c. Recycling sewage is comparatively easy in centralized systems
NPTEL Wastewater Treatment And Recycling Assignment Answer Week 2 2022
1. Which of the following parameters is NOT used to quantify the municipal wastewater generated from a city/town?
a. Total population of the city/town
b. Per capita water demand
c. Percentage of utilized water reaching the sewers
d. Stormwater received in the city
Answer :- d. Stormwater received in the city
2. The population of a planned city needs to be forecasted for a period of 50 years. Which of the following methods will generally result in the highest design population?
a. Arithmetic increase method
b. Geometric increase method
c. Incremental increase method
d. All these methods will result in the same population estimate
Answer :- b. Geometric increase method
3. The master plan method of population estimation is based on:
a. Population density and zone size
b. Annual birth/death rate and migration rates
c. Growth rate characteristics of living beings within limited space and economic constraints
d. Ratio of local to national population in the past few decades
Answer :- a. Population density and zone size
4. For design of sewers, estimates of per capita sewage generation is usually based on:
a. Design population
b. Design period
c. Recommended water use and wastewater generation pattern
d. Wear and tear of the sewers
Answer :- c. Recommended water use and wastewater generation pattern
5. Under which of the following population forecasting method, the maximum population of the city is limited by saturation population or carrying capacity?
a. Graphical method
b. Demographic method
c. Ratio method
d. Logistic growth method
Answer :- d. Logistic growth method
6. ‘Population growth is progressively increasing or decreasing’ is an assumption under which of the following method for population forecasting?
a. Incremental increase method
b. Arithmetic increase method
c. Geometric increase method
d. Growth Composition Analysis Method
Answer :- a. Incremental increase method
7. Among the following commercial institutions, the expected generation of wastewater (per user) is highest from:
a. Day Schools/Colleges
b. Hospitals with beds
c. Restaurants
d. Cinema Halls
Answer :- b. Hospitals with beds
8. The population recorded in 2001, 2011, and 2021 for a city was 4.2 lakhs, 5.6 lakhs, and 7.2 lakhs, respectively. Using the arithmetic increase method, the estimated population in the year 2051, would be:
a. 9.6 lakhs
b. 11.7 lakhs
c. 12.2 lakhs
d. 13 lakhs
Answer :- b. 11.7 lakhs
9. For a city with an initial population of 8 lakhs having an annual growth rate of 1.7 %, the estimated approx. population after 10 years would be: (Use the Geometric increase method and find the value to the nearest thousands)
a. 886 thousand
b. 925 thousand
c. 814 thousand
d. 1020 thousand
Answer :- c. 814 thousand
10. The inflow in sewers may exceed the design flow due to:
a. Sprinkling over the roads
b. Households using private water supplies
c. Water used in horticulture and landscaping
d. None of the above
Answer :- b. Households using private water supplies
11. The dry weather flow of a community is usually less than the per capita consumption due to:
a. Evaporation loss
b. Ground seepage
c. Sewer leakage
d. Any or all of the above
Answer :- d. Any or all of the above
12. Identify the CORRECT statement concerning flow estimation in sewer design.
a. The peak factor of a community typically decreases with the increase in population.
b. The minimum design flow in a sewer may vary from 1/3 to 1/2 of the average flow.
c. The maximum hourly flow is equal to one-third of the annual average daily flow.
d. Both a. and b.
Answer :- d. Both a. and b.
13. Typically, the peak factor of a community does NOT depend on:
a. Dry weather flow
b. Population density
c. Site topography
d. Supply hours
Answer :- a. Dry weather flow
14. If the average daily consumption of a town is 1,20,000 m3, the peak hourly demand will be:
a. 5,000 m3/ℎ
b. 7,500 m3/ℎ
c. 15,000 m3/ℎ
Answer :- 15,000 m3/ℎ
15. Determine the approximate quantity of wastewater generated from a city with total daily water consumption of 165 lpcd, if the conversion rate of water to wastewater is 85 % and the total population of the city is 165000.
a. 165 MLD
b. 27 MLD
c. 23 MLD
d. 85 MLD
Answer :- c. 23 MLD






